Browse by category
- Adaptive reuse
- Archaeology
- Arts and creativity
- Black heritage
- Buildings and architecture
- Communication
- Community
- Cultural landscapes
- Cultural objects
- Design
- Economics of heritage
- Environment
- Expanding the narrative
- Food
- Francophone heritage
- Indigenous heritage
- Intangible heritage
- Medical heritage
- Military heritage
- MyOntario
- Natural heritage
- Sport heritage
- Tools for conservation
- Women's heritage
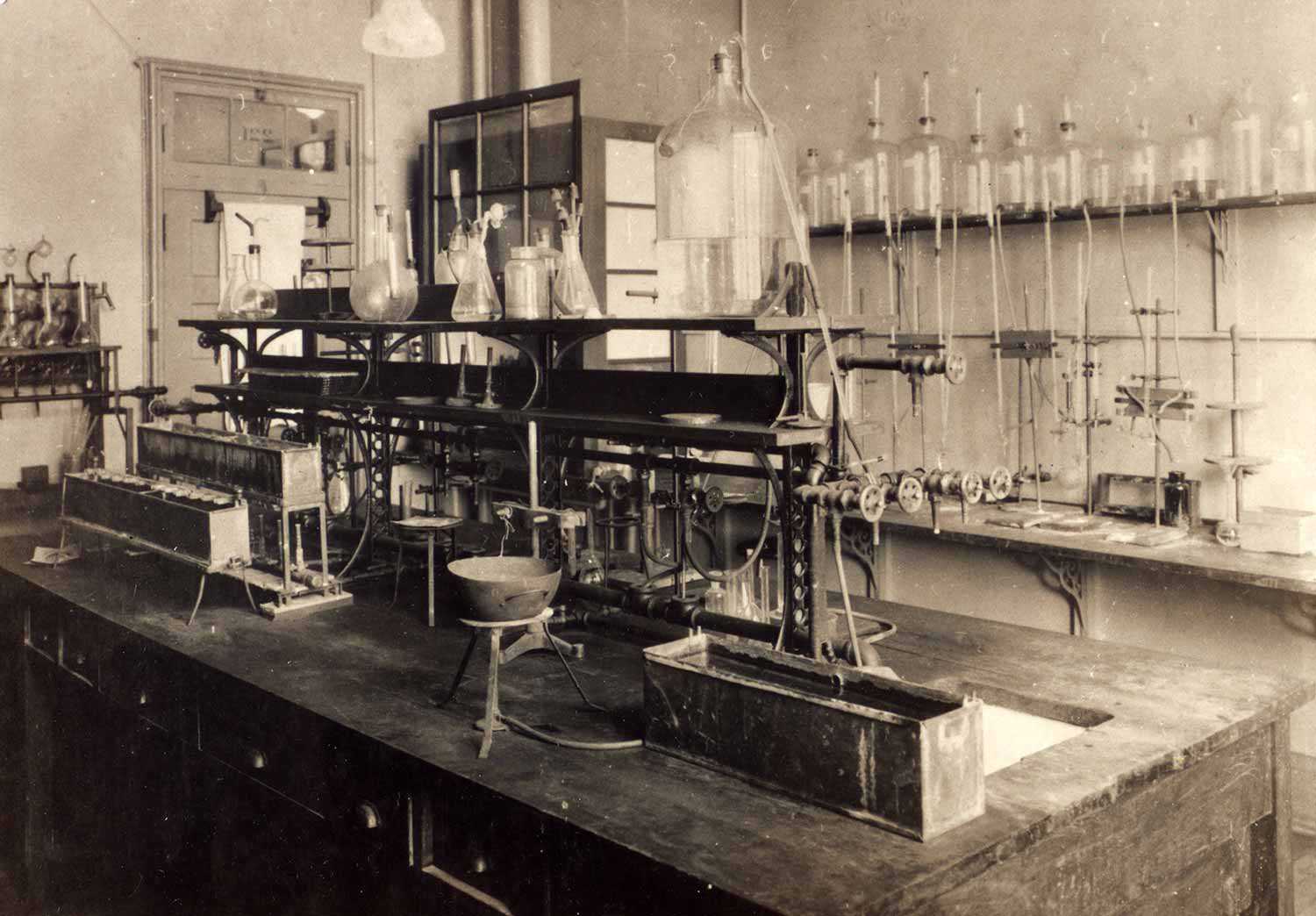
Doctors, discoveries and developments: Medical achievements and health care in Ontario
1824 Dr. Charles Duncombe opens the first medical school in Ontario, in St Thomas.
1839 College of Physicians and Surgeons of Upper Canada is formed.
1843 Christopher Widmer and John Rolph establish the Toronto School of Medicine (now the University of Toronto Medical School).
1861 Dr. Anderson Ruffin Abbott is the first Canadian-born doctor of African descent.
1867 The Canadian Medical Association is formed.
1869 A new College of Physicians and Surgeons of Ontario is incorporated by the Ontario Medical Act.
1871 Ontario College of Pharmacists is incorporated.
1875 Nurse Elizabeth McMaster opens a children’s hospital in an 11-room house in Toronto, which eventually becomes the Hospital for Sick Children.
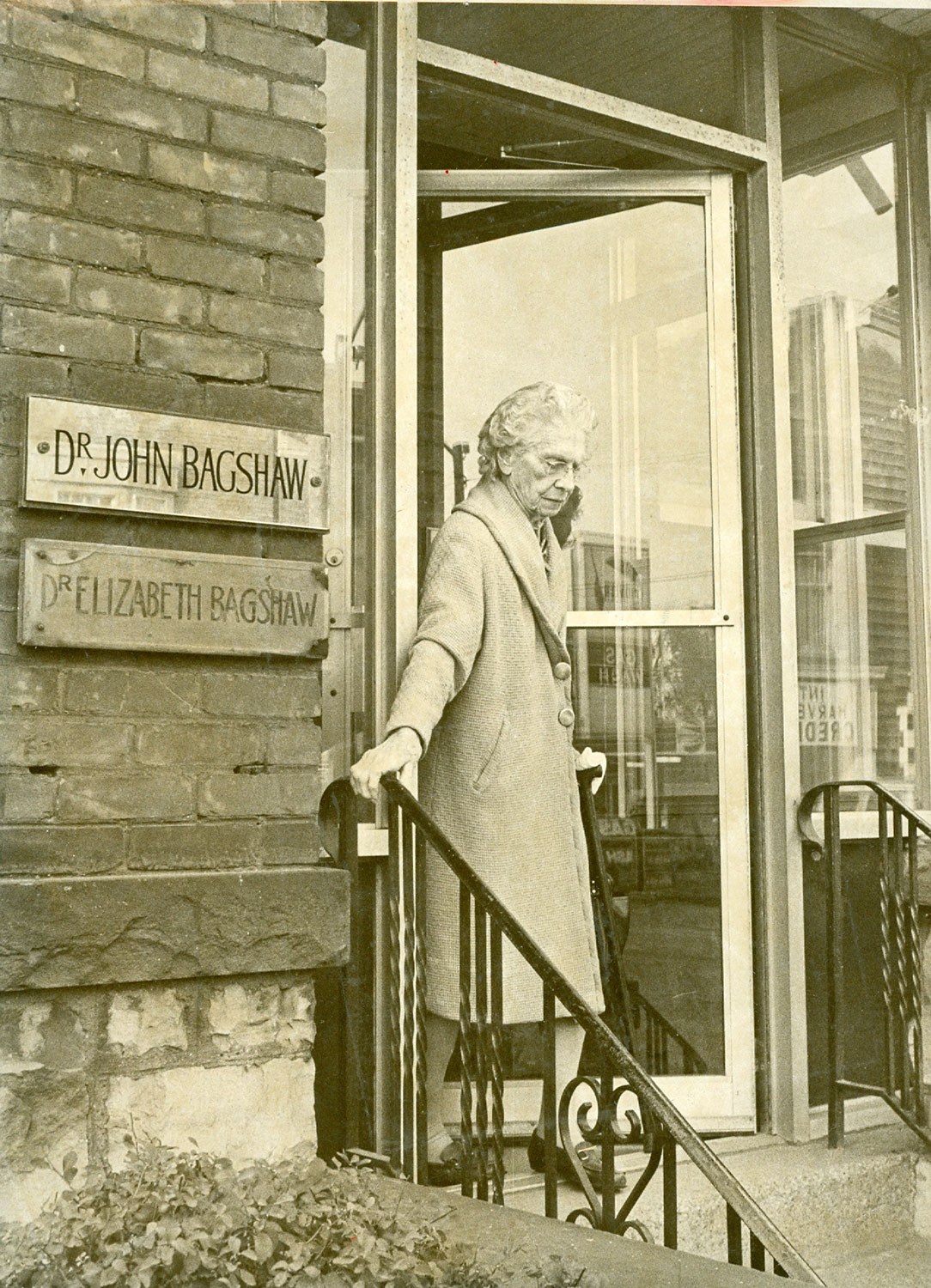
1880 The College of Physicians and Surgeons of Ontario grants Emily Stowe a license to practise medicine.
1882 Ontario Provincial Board of Health is created.
1883 Women’s Medical College is opened (later Women’s College Hospital).
1897 Daniel David Palmer of Port Perry, Ontario founds the field of chiropractic in Davenport, Iowa.
1911-12 Dr. Herbert Bruce opens Toronto’s Wellesley Hospital and its affiliated nursing school.
1918-20 Spanish influenza (Spanish flu) arrives in Ontario.
1919 Canada establishes the Department of Health as a response to the Spanish Flu crisis.
1921 Drs. Banting, Best, Collip and Macleod at the University of Toronto discover insulin as an effective treatment for diabetes.
1928-29 University of Toronto researchers discover heparin as a way to control blood clotting.
1930 The baby food Pablum is developed by Drs. Tisdall, Drake and Brown at Toronto’s Hospital for Sick Children.
1937 Dr. Gordon Richards founds the Canadian Association of Radiologists and establishes radiotherapy as a medical discipline.
1938 Ontario is the world’s first large jurisdiction to mandate the pasteurization of milk.
1940 The anti-gravity suit is developed by Wilbur R. Franks; the suits were used during the Second World War and all G-Suits now worn by air force pilots, astronauts and cosmonauts are based on his design.
1941 Dr. Jessie Gray becomes the first woman to become a fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons of Canada.
1943 Dr. Gordon Murray invents cardiac valve surgery.
1944 Ontario-born and-trained Dr. Albert Ross Tilley is made an Officer of the Order of the British Empire for his work and leadership in pioneering new techniques for treating British burn victims, soldiers and airmen.
1945 Dr. Edmund H. Botterell opens the Lyndhurst Lodge in Toronto – the first rehabilitation centre dedicated to spinal-cord-injured patients in North America.
1945 Dr. Gordon Murray invents an early dialysis machine for treatment of kidney disease.
1946 Veterans Centre at Toronto’s Sunnybrook Hospital opens.
1947 Dr. William T. Mustard develops the first successful cardiovascular surgery to correct a congenital heart defect in newborns.
1947 The discovery of the cobalt bomb leads to the production of radioactive cobalt-60 isotopes at Chalk River, Ontario; Harold E. Johns pioneers the use of cobalt-60 as a gamma ray source for radiation therapy in cancer cases.
1948 Dr. Gordon Murray develops interventricular septal defect repair for children born with holes in their hearts.
1949 Engineer John Hopps, from Ottawa’s National Research Council, develops the first artificial pacemaker.
1950 Dr. Vera Peters discovers that a significant proportion of people suffering with Hodgkin’s disease can be cured with high doses of radiation.
1952 Dr. John Callaghan discovers that hypothermia slows the human circulation system sufficiently to permit open-heart surgery.
1952 The Princess Margaret Hospital in Toronto is founded as the Ontario Cancer Institute.
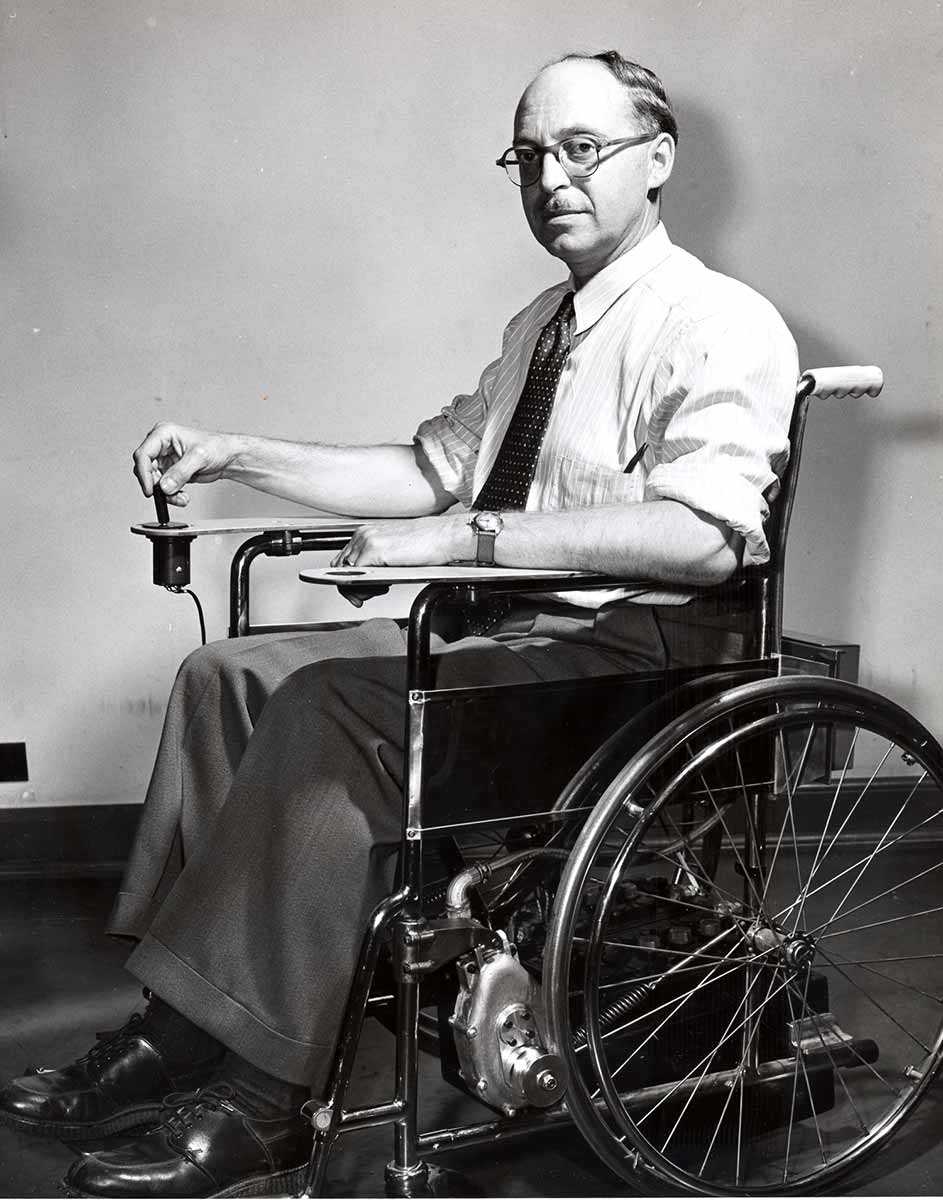
1953 Mechanical engineer, George Johann Klein from the National Research Council of Canada laboratories in Ottawa, invents the first electric wheelchair for quadriplegics.
1954 Colin McLaurin creates the McLaurin Hip Disarticulation Prosthesis at Sunnybrook Hospital in Toronto. This unique prosthesis relied on biomechanics to achieve stability and improve gait.
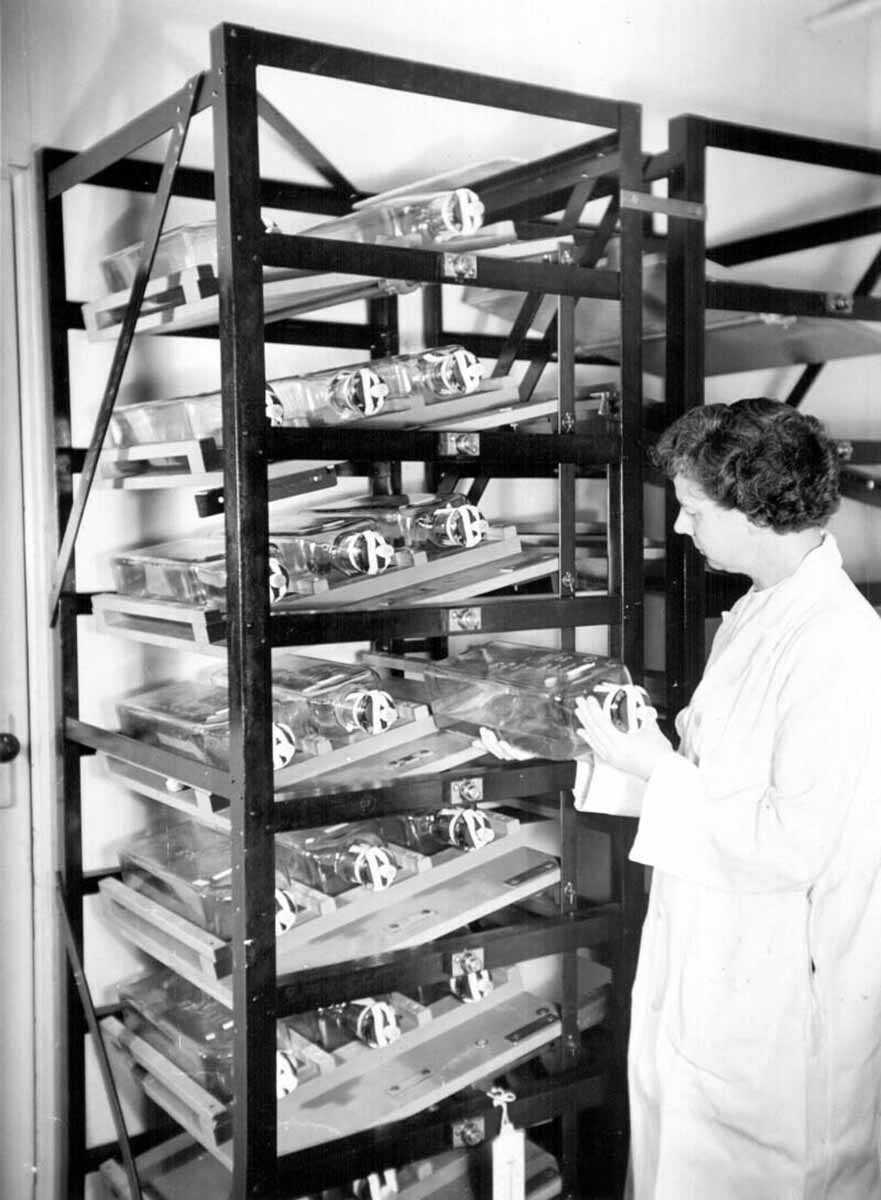
1954 Connaught Medical Research Laboratories produces some 3,000 litres (659 gallons) of poliovirus fluids for a massive field trial of the Salk inactivated polio vaccine.
1958 The drug vinblastine is discovered at the University of Western Ontario by Drs. Robert Noble and Charles Beer; used with other drugs, it has a major impact on controlling the growth of some types of cancer.
1958-75 Dr. Vera Peters proves that a lumpectomy, followed by radiation, is as effective a treatment as radical mastectomy.
Early 1960s Drs. Ernest McCulloch and James Till identify and isolate transplantable stem cells in mice; this discovery allows for the study of individual stem cells in human adult bone marrow.
1966 The Ontario Government introduces the Ontario Medical Services Insurance Plan – the province’s first universal health-care system that insures physicians’ service. By 1972, the plan is known as OHIP. Every resident of Ontario is entitled to access free emergency and preventive care.
1984 The Ross Tilley Burn Centre opens at Toronto’s Wellesley Hospital.
1986 Dr. Wilbert Keon is the first Canadian doctor to implant an artificial heart.
1986 The longest physicians’ strike in Canada occurs in Ontario in 1986, when the Ontario Medical Association called a work stoppage to protest the government’s ban on extra billing.
1989 Canadian volunteers first come together to create a Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders (MSF) association; MSF in Canada formally joins the international movement in 1991.
1989 Dr. Lap-Chee Tsui discovers the gene responsible for cystic fibrosis. This is considered the most significant breakthrough in human genetics in half a century.
1990s Dr. John Dick, from the Ontario Cancer Institute, proves the existence of cancer stem cells – a type of cancer cell responsible for the growth and spread of the disease.
1994 Ontario is the first province to regulate midwifery as part of the Regulated Health Professions Act. Elsie Cressman, native of New Hamburg, Ontario is awarded the Order of Ontario for her role in the advocacy of midwifery.
1998 The role of nurse practitioner is regulated in Ontario.
1999 Dr. W. Douglas Boyd, a cardiothoracic surgeon in London, Ontario, performs the world’s first totally closed-chest, computer-enhanced, robotics-assisted coronary bypass operation on a beating heart.
Late 1990s Drs. Anthony Lang and Andres Lozano develop deep brain stimulation (DBS) at Toronto Western Hospital; DBS has improved the lives of hundreds of people suffering from Parkinson’s disease.
2003 The SARS epidemic hits Canada; approximately 85 per cent of all Canadian SARS cases occurred in Ontario; in total, 44 people in Canada died from SARS, approximately 400 became ill and 25,000 Toronto residents were placed under quarantine.
2005 Dr. Endel Tulving from Toronto’s Baycrest Centre is awarded the Canada Gairdner International Award for pioneering research in the understanding of human memory, and for providing the necessary framework within which findings in neuroanatomy, neurophysiology and neuropharmacology can be integrated.
2006 The Traditional Chinese Medicine Act establishes the College of Traditional Chinese Medicine Practitioner and Acupuncturists of Ontario.
2007 The title of Nurse Practitioner becomes a protected title in Ontario. Nurses in four specialty areas of medicine can use this title: primary health care, pediatrics, adult and anesthesia.
2010 Sioux Lookout Meno Ya Win Health Centre is established – an extended-care facility that merges traditional First Nations and modern healing practices.
2011 Ontario Stem Cell Initiative is launched at the University of Toronto, bringing together 65 scientists for a provincewide partnership to make Canada an international leader in this technology.
By 2011, Canadians’ life expectancy at birth has grown from 57.1 in 1921 to 81.7.
2015 Canadian researchers launch the world’s first clinical trial of a novel investigational therapy that uses a combination of two viruses to attack and kill cancer cells and stimulate an anti-cancer immune response.
2016 50th anniversary of the province’s first universal health-care system.
2016 First successful hand transplant in Canada is performed at Toronto Western Hospital, a part 2015 of the University Health Network.